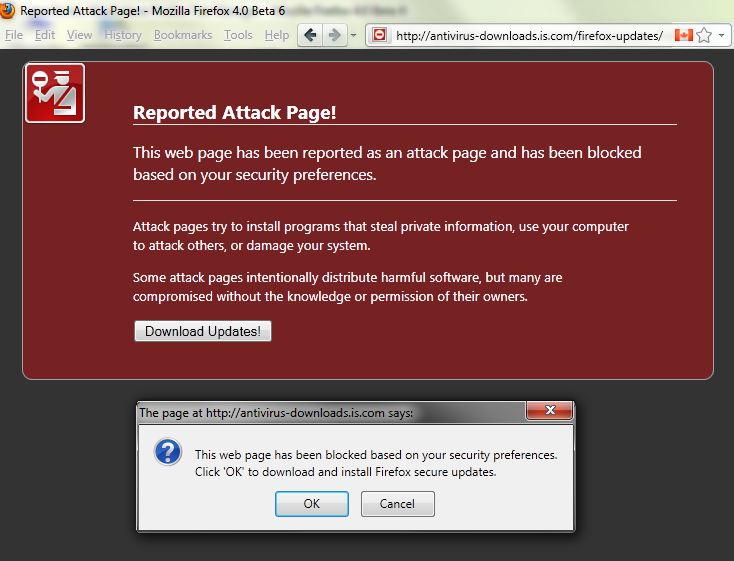
Coinbase Security and Google security researcher Samuel Gross discovered a vulnerability in Mozilla Firefox browser that could manipulate Javascript objects. It has already been used to attack users of cryptocurrency. This is reported on Medium .
The zero-day vulnerability received a CVE-2019-11707 identifier, and in Firefox, the bug was assigned a critical or highest threat level.
"Critical vulnerability – it can be used to launch an attacker's code and install software that does not require user interaction, except for normal viewing."
In fact, the attackers could force users to go to malicious sites and thus be able to execute arbitrary code on the devices of their victims. The scammers who used the bug could install programs, view, change or delete data, as well as create new accounts.
Users are urged to upgrade as soon as possible to the new version of Firefox 67.0.3 and Firefox ESR 60.7.1, in which the vulnerability is fixed.
Context: https://t.co/EQX4Ev42tx
– Samuel Groß (@ 5aelo) June 19, 2019
In addition, malicious applications for the Android OS were found. They could steal one-time two-factor authentication passwords using a notification system.
2FA & OTP codes.
It intercepts SMS notifications.
Discovered fake cryptocurrency exchanges with such functionality on the Play Store. https://t.co/t5Vtm3DrJW– Lukas Stefanko (@LukasStefanko) June 17, 2019
ESET researcher Lukash Stefanko has identified a number of applications (BTCTurk Pro Beta and BtcTurk Pro Beta), posing as the Turkish cryptocurrency exchange BtcTurk. They could steal account data and use it in services protected by two-factor authentication.
Note that at the beginning of the year, Google imposed restrictions on applications by banning them from accessing SMS messages and call logs without serious justification. However, the attackers were able to circumvent these limitations: applications request permission to check and manage notifications.
Once it was received, users were asked to enter their credentials from various cryptocurrency services in fake forms. The collected information was transferred to the attackers server, and they got access to notifications from other applications. It is noteworthy that fraudsters could also turn off the sound, notifying of incoming notifications, so that the victims did not even know about unauthorized intervention.
Thus, the researcher discovered filters that distinguish a kind of target applications, whose names contain the keywords gm, yandex, mail, k9, outlook, sms and messaging.
Recall, recently, analysts at ESET found a fake Trezor Mobile Wallet app in the Google Play store, disguised as a popular wallet and stealing users' cryptocurrency.
Subscribe to BlockchainJournal news on Facebook !
BlockchainJournal.news
BlockchainJournal.news